Conjunctivitis
Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is an irritation or inflammation of the conjunctiva, which covers the white part of the eyeball. It can be caused by allergies or a bacterial or viral infection. Conjunctivitis can be extremely contagious and is spread by contact with eye secretions from someone who is infected.
Symptoms
One or both eyes may be affected and symptoms can include: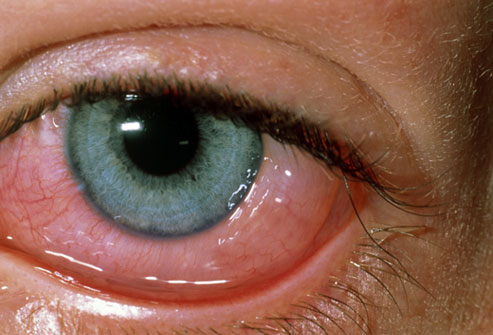
- Itchiness
- Redness
- An uncomfortable gritty feeling
- Discharge. Can form a crust during the night and make it difficult to open the eye in the morning
- Excessive watering of the eye(s)
- Swelling of the eyelid
- Light sensitivity
Causes
There are many causes of conjunctivitis including:
- Viruses
- Allergies
- Bacterial infections
- Chemical injury
- Foreign objects in the eye
- Use of contact lenses over an extended period of time
- Babies – blocked tear duct
- Less common causes are chlamydia and parasites
Prevention
If you know someone who is suffering from conjunctivitis, avoid contact with them. Children with this infection should not attend school until they are fully recovered.
Good hygiene is extremely important, as it will help to prevent the spread of conjunctivitis. Some suggestions include:
- Frequent change of pillowcases

- Do not touch your eyes or around them with your hands
- Wash hands frequently (and make sure children wash their hands thoroughly)
- Handle and clean contact lenses properly or avoid contact lenses altogether whilst infection is active
- Don’t share towels or tissues
- Don’t share eye cosmetics
- Discard any makeup which has been used on infected eyes
Treatment
Allergic conjunctivitis (AC)
If an allergy is causing irritation, a doctor may prescribe eye drops containing medications that control allergic reactions (e.g. antihistamines and mast-cell stabilisers) or drugs that control inflammation.
The severity of AC can be reduced if the cause is known and deliberately avoided, although this may not always be possible.
Bacterial conjunctivitis (BC)
Antibiotic eye drops may be prescribed for BC. Even without medication, the infection should ease after several days.
An antibiotic eye ointment is sometimes used in children as this can be easier to administer, although it can blur vision for a short time after application. In either case, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and use the antibiotics for the recommended period to prevent a recurrence of the infection. Do not stop the treatment early, even if the eye seems better.